What is Pecking Order Theory:
Pecking Order theory is based on Asymmetric information, which refers to a situation in which different parties have different information. In a firm, managers will have better information than investors.
This theory states that firms prefer to issue debt when they are positive about future earnings. Equity is issued when they are doubtful and internal finance is insufficient.
The pecking order theory argues that the capital structure decision is affected by manager’s choice of a source of capital that gives higher priority to sources that reveal the least amount of information.
Myers has given the name ‘PECKING ORDER’ theory as here is no well-defined debt-equity target and there are two kind of equity internal and external.
Now Debt is cheaper than both internal and external equity because of interest. Further internal equity is less than external equity particularly because of no transaction/issue cost, no tax etc.
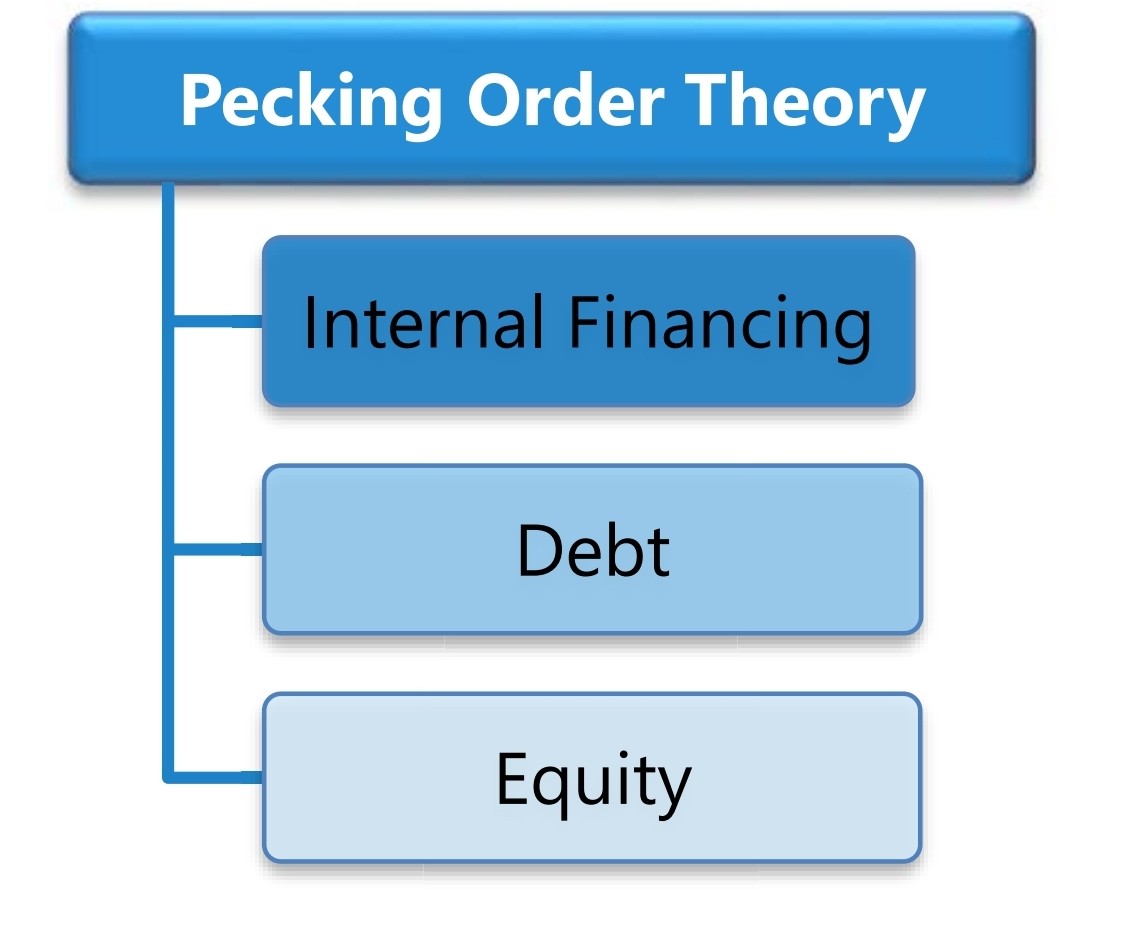
Pecking order theory suggests that managers may use various sources for raising of fund in the following order:
- Managers first choice is to use internal finance.
- In absence of internal finance, they can use secured debt, unsecured debt, hybrid debt etc.
- Managers may issue new equity shares as a last option