Digitalization is revolutionising the operations of tax administrations by significantly enhancing their capacity to gather, process, and oversee tax-related information. A notable instance of this is electronic invoicing (e-invoicing), which facilitates the automated exchange of billing data between businesses and tax authorities. Motivated by its potential to enhance tax compliance and lower expenses, over 50 countries worldwide have embraced e-invoicing.
The growth of digital payments has considerably affected the examination of income tax, with governments and tax authorities relying more on digital transactions to improve transparency and address tax evasion. This transformation is mainly fuelled by the improved traceability of transactions, which boosts tax compliance and revenue generation.
Here are some important points on how digital payments affect income tax scrutiny:
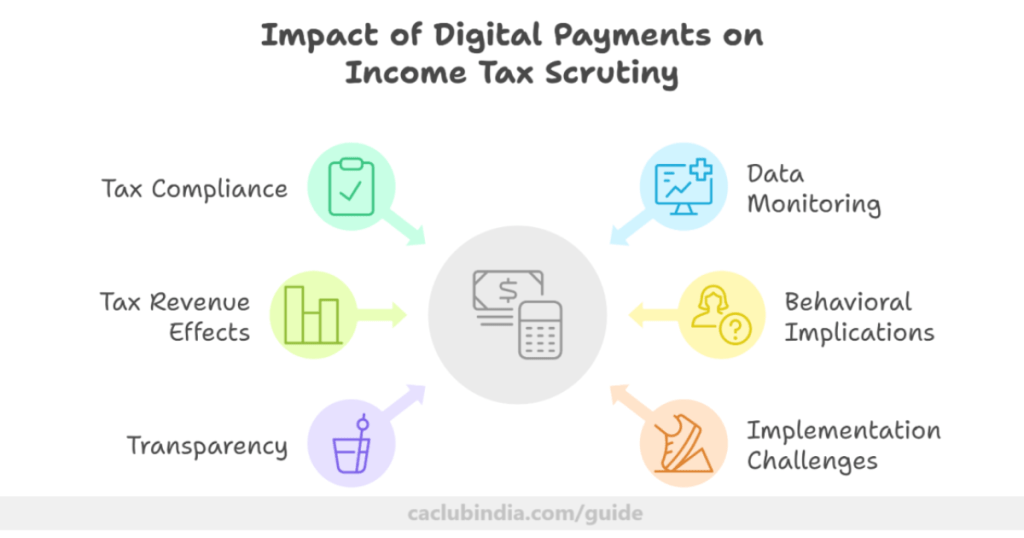
Improved Tax Compliance
Digital payments establish a clear record of transactions, making it more challenging for individuals and businesses to avoid taxes. Research shows that the use of electronic payment systems enhances tax compliance. For example, studies indicate that when transactions are documented digitally, tax authorities can more easily verify reported income against actual transactions, thereby lowering the chances of tax evasion.
Monitoring and Reporting of Data
The incorporation of digital payment systems enhances data collection and tracking capabilities. Payment processors and banks frequently need to share transaction information with tax authorities, facilitating the comparison of reported sales against actual sales data. This level of oversight can discourage individuals from underreporting their income or participating in unreported economic activities. Additionally, leveraging digital tools streamlines the reconciliation process for taxpayers, as automated systems are far more effective at tracking income and expenses compared to traditional manual methods.
Effects on Tax Revenue
The shift towards digital payments has been associated with a rise in overall tax revenue. With a growing number of transactions occurring electronically, governments are better able to record a greater share of economic activity that was previously untracked. This phenomenon is particularly noticeable in countries such as India, where the government has promoted digital transactions to boost GST revenue and improve overall tax compliance.
Behavioural Implications
Although the advantages of digital payments are evident, there are also behavioural factors to take into account. The convenience of digital transactions might cause some taxpayers to become lax regarding their reporting obligations. Consequently, tax authorities need to develop systems that promote accurate reporting and reduce the likelihood of errors in tax filings.
Enhanced Transparency and Trackability
Digital payments create clear and readily available records of transactions that tax authorities can easily audit. This heightened transparency diminishes the chances of income underreporting, as businesses find it more difficult to conceal cash transactions from oversight. Financial intermediaries engaged in electronic transactions frequently submit data directly to tax authorities, facilitating a dependable source of information that can be cross-verified with taxpayer declarations.
Challenges in Implementation
The success of digital payment systems in improving tax compliance depends on the ability of tax authorities to effectively analyze the data generated. Many governments may not have the necessary resources or technology to manage the large volumes of data produced by electronic transactions. Research indicates that making the adoption of digital payment systems mandatory results in better compliance rates than when participation is voluntary. When taxpayers are obligated to use electronic payments, compliance tends to see a substantial improvement.
International Trends and Case Studies
Countries such as India have observed notable improvements in tax compliance as a result of initiatives designed to encourage digital payments, especially following demonetization efforts that promoted electronic transactions. Additionally, the pandemic has expedited the move toward digital payments, with both businesses and consumers increasingly opting for contactless transaction methods. This transition has underscored the vital role of digital payment systems in contemporary economies and their contribution to boosting compliance.
Conclusion
Digital payments greatly improve the transparency and accountability of financial transactions, which in turn fosters better tax compliance. Nonetheless, taxpayers are required to keep thorough records and remain informed about tax laws to evade possible audits. The move towards digital payments has significant effects on income tax oversight, promoting transparency and compliance, while also introducing challenges in terms of implementation and enforcement. As governments adapt to this change, effectively utilizing technology will be essential to fully harness the advantages of digital transactions for tax administration