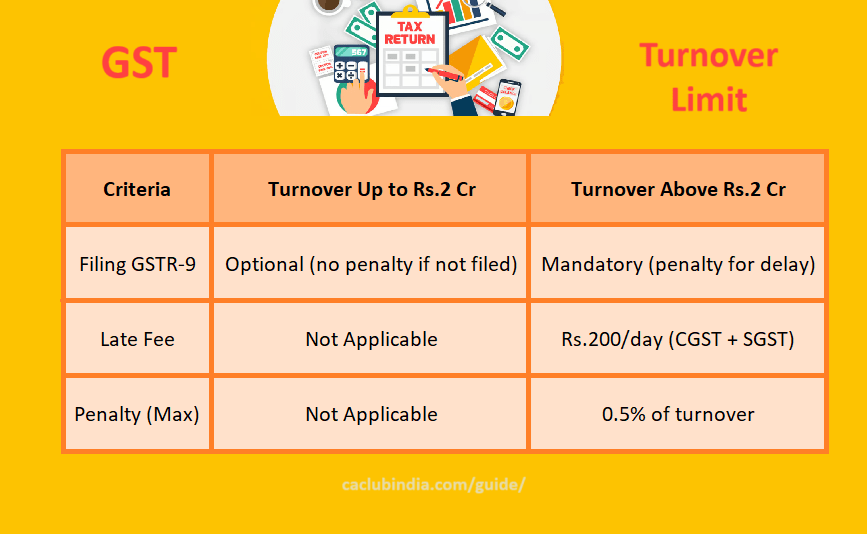
The turnover limit for filing GSTR-9 (Annual Return) under GST is as follows:
Turnover Limit for GSTR-9
Mandatory Filing
If your aggregate turnover exceeds Rs.2 crores in a financial year, you are required to file GSTR-9.
Optional Filing
If your aggregate turnover is up to Rs.2 crores, filing GSTR-9 is optional.
The government introduced this relaxation to reduce the compliance burden on small taxpayers.
What is Aggregate Turnover?
Definition
Aggregate turnover is the sum of all taxable and non-taxable supplies, exempt supplies, exports, and inter-state supplies (all calculated on an all-India PAN basis).
Inclusions
- Taxable supplies (whether within the state or inter-state)
- Exempt supplies (like nil-rated, zero-rated, and non-GST supplies)
- Export of goods and services
- Inter-state supplies between different GSTINs under the same PAN
Exclusions
- GST (CGST, SGST, IGST, and Cess)
- Value of inward supplies on which reverse charge is applicable
Due Date for Filing GSTR-9
The normal due date is 31st December following the end of the financial year.
Example: For FY 2023-24, the due date would be 31st December 2024 (unless extended).
Late Fees and Penalties
If GSTR-9 is not filed by the due date:
- Late Fee: Rs.100 per day under CGST + Rs.100 per day under SGST (total Rs.200/day).
- Maximum Penalty: 0.5% of the turnover in the state or union territory.
- No Late Fee for Optional Filing: If your turnover is up to Rs.2 crores and you choose not to file, there is no late fee or penalty.
Components of GSTR-9
GSTR-9 is a summary of the returns (GSTR-1, GSTR-3B) filed during the year. It has the following sections:
- Part 1: Basic details (GSTIN, financial year, trade name, etc.)
- Part 2: Details of outward supplies (taxable, exempt, exports, etc.)
- Part 3: Details of input tax credit (ITC) availed and reversed
- Part 4: Details of tax paid (CGST, SGST, IGST, cess)
- Part 5: Details of transactions of the previous financial year reported in the current year
- Part 6: Other information (demands, refunds, HSN summary, etc.)
Who requires to File GSTR-9?
- Normal Taxpayers including SEZ units and developers.
- Composition Scheme Dealer [can file Annual Return in Form GSTR-9A].
Who is Exempt from Filing GSTR-9?
- Composition Dealers: They file GSTR-9A instead.
- Casual Taxpayers, Input Service Distributors (ISD), Non-Resident Taxpayers, and TDS/TCS Deductors: Not required to file GSTR-9.
How to Calculate Turnover for GSTR-9?
To calculate if you are required to file GSTR-9, you need to determine your aggregate turnover.
Formula for Aggregate Turnover:
Aggregate Turnover = Taxable Supplies + Exempt Supplies + Exports + Inter – State Supplies (all PAN-based GSTINs)\text{Aggregate Turnover} = \text{Taxable Supplies} + \text{Exempt Supplies} + \text{Exports} + \text{Inter-State Supplies (all PAN-based GSTINs)} Aggregate Turnover=Taxable Supplies + Exempt Supplies + Exports + Inter – State Supplies (all PAN-based GSTINs)
- Use the GSTR-3B data to get details of taxable and exempt supplies.
- Include turnover from all GSTINs under the same PAN (not just one GSTIN).
Practical Example
Scenario:
- You operate 2 businesses in 2 different states (GSTIN-1 and GSTIN-2) under the same PAN.
- Turnover of GSTIN-1: Rs.1.3 crore
- Turnover of GSTIN-2: Rs.1.1 crore
- Total Turnover = Rs.1.3 crore + Rs.1.1 crore = Rs.2.4 crore
Since the total turnover is more than Rs.2 crore, you are required to file GSTR-9.
Click Here – GSTR-9: Claiming ITC for Cross-Year Invoices For FY 2023-24


