F and O – Futures and Options is a non speculative business which are types of financial derivatives used in trading.
With the rise of retail participation in the stock market, Futures & Options (F&O) trading has become a popular avenue for both full-time and part-time traders in India. The high leverage and potential for quick gains have attracted many individuals – but what often gets overlooked is the taxation aspect of F&O trading.
According to Section 43(5) of the Income Tax Act, trading in futures and options (F&O) is classified as a business activity. Consequently, any profits or losses incurred from F&O trading are treated as non-speculative business income for tax purposes, rather than capital gains.
Difference between Speculative and Non Speculative Income
| Basis | Speculative Trading | Non-Speculative Trading |
| Meaning | Buying and selling of assets with the intention of making quick profits, often without actual delivery of the asset. | Trading that involves derivatives or delivery-based trades which are not considered speculative under law. |
| Settlement | Not settled by actual delivery of goods or securities. | May or may not involve delivery, but is recognized under tax rules as non-speculative. |
| Examples | Intraday equity trading (buy and sell same stock on same day). Betting on short-term price movements without delivery | F&O trading on recognized stock exchanges. Delivery-based share trading or commodity F&O trading (even without delivery) |
| ITR Form | ITR-3 | ITR-3 |
| Books of Accounts | Required if turnover exceeds limits | Required if turnover exceeds limits |
| Tax Audit | Applicable based on turnover and profit % | Same rules apply |
Calculation of Turnover
| Segment | How to Calculate Turnover |
| Futures | Add absolute value of all profits and losses |
| Options | Add absolute value of profits and losses + premium received on options sold |
For Example
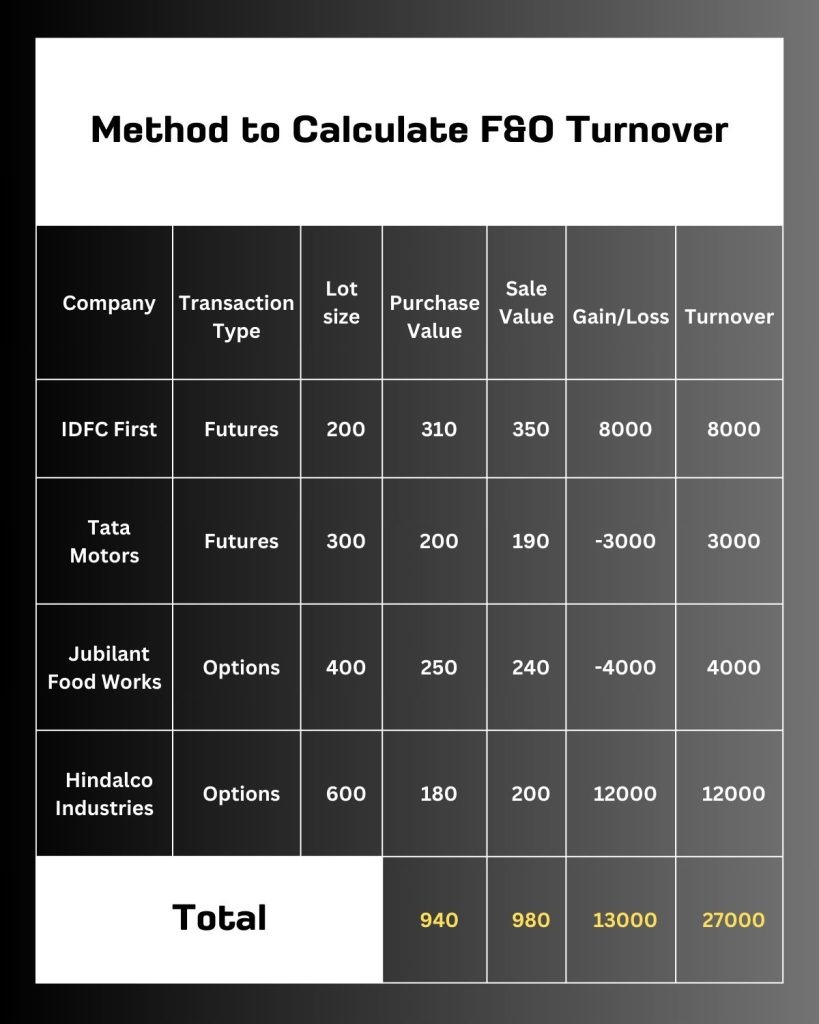
Here,
Sum of profits = 8,000 + 12,000 = 20,000
Sum of absolute losses = 3,000 + 4,000 = 7,000
Absolute Turnover = 20,000 + 7,000 = 27,000
Applicability of Tax Audit
Tax audit is required if:
- Turnover exceeds ₹10 crore (if 95%+ transactions are digital).
- OR turnover is above ₹1 crore and profit < 6% of turnover (and you don’t opt for presumptive taxation).
Click here to know the slab rates.
Allowable Expenses
As F&O income is classified as business income, traders are eligible to deduct expenses directly and solely incurred for their trading activities. These deductible expenses include brokerage charges, commissions paid to brokers, subscriptions for trading journals, telephone and internet expenses, professional advisory fees, and other trading-related costs.
Set off and Carry Forward
Carry Forward of Business Losses
To carry forward any business loss, ensure timely filing of income tax returns by July 31st for non-audit cases and September 30th for audit cases.
Speculative Losses
- Can be carried forward for a maximum of 4 years.
- Can only be offset against speculative gains within that 4-year period.
Non-Speculative Losses
- In the same year they are incurred, non-speculative losses can be offset against any business income excluding salary income. This includes bank interest, rental income, and capital gains.
- Unabsorbed non-speculative losses can be carried forward for up to 8 subsequent years.
- In the years they are carried forward, these losses can only be offset against non-speculative business gains.
Set off
Speculative (Intraday equity) loss can’t be offset with non-speculative (F&O) gains, but speculative gains can be offset with non-speculative losses.
Advance Tax
- Applicable if tax liability > ₹10,000.
- F&O traders must pay advance tax in four installments (June, Sept, Dec, March).
- Interest under 234B/234C if advance tax is not paid on time.
TDS implementation
Profits from F&O transactions are now subject to Tax Deducted at Source (TDS). This means taxes will be directly deducted before the net profit is credited to the trader’s account. This measure aims to ensure timely tax collection and minimize tax evasion.
GST Applicability
GST is not applicable to F&O trading on recognized exchanges like NSE/BSE. However, GST may be levied on transaction charges, brokerage, and STT.
Securities Transaction Tax
The Securities Transaction Tax (STT) on the sale of futures contracts has been increased to 0.02% from the previous rate of 0.0125%. Similarly, the STT on the sale of options contracts has risen from 0.0625% to 0.1%.
FAQs
F&O trading is treated as non-speculative business income, not capital gains, under Section 43(5) of the Income Tax Act.
A tax audit is required if:
1. Turnover exceeds ₹10 crore (if 95%+ digital transactions), or
2. Turnover exceeds ₹1 crore and profits are less than 6% of turnover.
Yes. If your total tax liability exceeds ₹10,000 in a financial year, you must pay advance tax in four installments.
Yes. Salaried persons can trade in F&O and must file ITR-3 for combining salary and business income.
Yes, if turnover exceeds ₹10 lakh or if required under Section 44AA. It’s also advisable to maintain records for better audit and compliance.
1. For non-audited traders: 31st July 2025
2. For audited cases: 31st October 2025