A signature you make on an important document is your way of acknowledging or authenticating that document and to self-certify that this document has your approval, similarly, a digital signature is an electronic signature that authenticates an electronic or virtual document. Not only that, a digital signature acts as a unique virtual fingerprint. It is used to authenticate the validity of any electronic document, message, or software. The importance of digital signatures is obvious with the rapid escalation in virtual documents, messages, and important software and applications. It is valid proof of the authenticator’s identity and data integrity.
How Exactly Does It Work?
The most important aspect of a digital signature is a mathematical algorithm. This algorithm is used to validate the integrity of data and also in ensuring that there is no tampering with the data in the process of transit. This algorithm creates a virtual fingerprint that is unique to an entity and acts as an acknowledgment of that person’s approval of the data. Digital signatures work through public-key cryptography, wherein a key pair system is used that has a public and a private key. This key system encodes and decodes the data. The private key is used to encode the data and is available only to the signer, whereas the public key works to decode or decrypt the data for the receiver. This system ensures that there is no distortion during transit and also keeps the data secure. It can be easily inferred that the basic functions of such a signature are Encryption and Authentication.
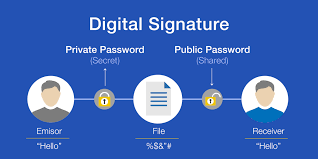
An individual is assigned a unique virtual identity from a trusted service provider. Thus, the functioning of a digital signature is characterized by its Creation, Encryption, Time Stamp, and Keys Generation. Each digital signature is created using a secret file and encrypted with an algorithm. They are also marked with a timestamp when the document is signed and if there is any distortion after signing, the signature becomes invalidated. The generation of keys and algorithms is done by a Certified Authority. A Public Key Infrastructure involves regulations, rules, protocols, and systems that are instrumental in developing authentication and validation in the signatures. These are accepted formats that ensure high-level security.

Different Types Of Digital Signatures
From the technological point of view, there are three types of signatures-
- Simple Signature in which the encryption is not secured.
- Basic Signature is very similar to the Simple Signature
- Advanced Signature is the most secure and standardized digital signature that has the same legal value as that of a wet paper
In terms of certification, there are three types of digital signature:
- Class 3 certificate Signature- This kind of DSC is used for filing documents at the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Income Tax Portal, GST portal, and many more common filing platforms.
- Class 3 Certificate Signature with Encryption - It contains an extra feature of encryption which is used on government tenders' website. It also includes the feature of Class III Signature
- Class DGFT - This is used on the DGFT website for claiming export incentives.








 CAclubindia
CAclubindia
