Concept of Time of Supply
Tax is leviable under GST upon occurrence of the Taxable event, Supply. But the tax so levied shall be liable to pay at the time as determined by the Time of Supply provisions. The Tax rates, Exchange rates, exemptions and abatements keep changing from time to time. So it is necessary that uniform or a fixed principles shall be laid down to determine the time when the charging event takes place.
The "Time of Supply" provisions are laid down under the CGST Act, 2017 separately for Goods and Services.
A) Section 12 of CGST act, 2017 determines the "Time of supply of goods"
B) Section 13 of CGST act, 2017 determines the "Time of supply of services"
C) Section 14 of CGST act, 2017 determines the "Time of supply of goods or services in case of change in rate"
In our previous article we discussed about Time of supply of goods in detailed. Now, we will start decoding for Time of supply of services and change in rate cases.
Time of Supply in case of Services:
Time of supply of services shall be determined differently in each of the 5 scenarios as discussed below:
A) General scenario/Forward Charge Scenario:
The time of supply can be determined as follows:
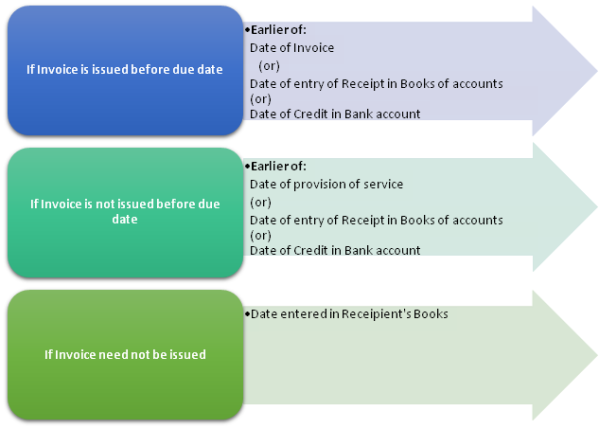
Exception: If an amount upto Rs.1000/- is received in excess of amount in Tax invoice then Time of Supply need not be Date of Receipt. Supplier can even opt Date of Invoice as "Time of Supply"
Reverse Charge Scenario:
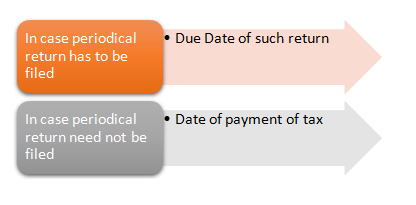
Usually, the GST liability is to be discharged by the service provider. However, in specific cases, the liability to pay tax is imposed on the recipient of the services instead of the service provider. This method of charging of tax liability is known as Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM). The CGST act, 2017 passed in Parliament yesterday provide that in cases of supply of services by an unregistered supplier to a registered person, GST shall be paid by the recipient under RCM.

*Exception: - If any of the above dates are not identifiable, Date of Entry of transaction in Recipient Books
Interesting point to be noted here is the concept of "Associated Enterprise" is referred to only in the context of time of supply whereas definition of related person is referred in the context of supply and valuation which includes associated enterprises also.
A) Supply of Vouchers:
In the CGST act, 2017 passed in Parliament yesterday the Definition of vouchers is given as "an instrument where there is an obligation to accept it as consideration or part consideration for a supply of goods or services or both and where the goods or services or both to be supplied or the identities of their potential suppliers are either indicated on the instrument itself or in related documentation, including the terms and conditions of use of such instrument"
In simpler terms Voucher is a small printed piece of paper that entitles the holder to a discount, or that may be exchanged for goods or services. e.g.: coupons, pass, token etc.,

An exact replica of the provision is also specified under section 12 in relation to time of supply of goods. So, one can infer that ‘vouchers exchangeable for goods" and ‘vouchers exchangeable for services" as distinct and separate class of transactions. But there will be certain class of Vouchers which can be exchanged for goods as well as services at the option of holder. In such scenarios supply cannot be identified at the time of issue so date of redemption of voucher is the key.
To summarize:
- If supply is identifiable at the time of issue and related to goods then Time of supply is "Date of issue of Voucher"- Sec 12
- If supply is identifiable at the time of issue and related to services then Time of supply is "Date of issue of Voucher" -sec13
- If supply is not identifiable at the time of issue then Time of supply is "Date of redemption of Voucher".
C) Addition in Value of Supply by way of interest late fee or penalty:
Time of supply in relation to such addition is "Date of Receipt of such amount"
D) Residuary Clause:
Time of supply under this residuary provision is applicable only when the other provisions are found to be inapplicable and not merely when there is some difficulty in determining the facts that are sought for by the relevant provision.
Time of Supply in case of Change in Rate of Tax:
To determine Time of supply in case both goods and services when there is a change in rate of tax provisions of section 14 shall be applied instead of applying provisions of section 12 or section 13. Date of supply, Date of Invoice and Date of payment are the three criteria which can decide the Time of supply and applicable rate. The following table serves the purpose:
|
Date of Supply (Criteria 1) |
Date of Invoice (Criteria 2) |
Date of Payment (Criteria 3) |
Applicable Rate |
Time of Supply |
|
Before |
Before |
After |
Old Rate |
Date of Invoice |
|
Before |
After |
Before |
Old Rate |
Date of Payment |
|
Before |
After |
After |
New Rate |
Date of Invoice (or) Date of Payment whichever is earlier |
|
After |
Before |
After |
New Rate |
Date of Payment |
|
After |
After |
Before |
New Rate |
Date of Invoice |
|
After |
Before |
Before |
Old Rate |
Date of Invoice (or) Date of Payment whichever is earlier |
The simple logic here is that -"Among the three dates if new rate is prevailing on the majority dates then new rate and if old rate prevailing on the majority dates then old rate."Now once the rate is determined then consider dates having determined rate only and among those dates, Date of Invoice or Date of Payment whichever is earlier shall be Time of supply.
This article is an endeavor to share some learnings obtained. The views expressed are of the author and are intended solely for informational purpose only. Though due care is taken while preparing the document, possibility of errors cannot be ruled out Expert guidance, where required and user discretion is highly recommended.
The author can also be reached atcachaitanyakumar@gmail.com.








 CAclubindia
CAclubindia
