Introduction:
From the last two years, you might have heard a lot about blockchain but the moment you browse for it over the internet, you get typical and more technical results which may not be simple to understand for someone from a non-technical background. In fact, blockchain is a purely technical concept thus getting technical theories on the internet about it is very common. Nowadays much noise is in the market for bitcoins that is why the blockchain concept is in trend. Yes!! It is a kinda revolution in the field of technology. But this is new technological concept and loopholes still exist. We will further discuss in detail.
Bitcoin vs Blockchain
We often confuse between these two terms and consider them to be one and the same but these are different significantly. Bitcoins are a product of Blockchain technology. Blockchain is a wider term than that of bitcoins. Bitcoins is a successful implementation of blockchain technology. In the Indian market rumors of failing of bitcoins are in debates and people are blaming blockchain for that. A drop in the valuation of bitcoins is totally dependent upon the free play of market forces. One cannot hold technology responsible for this, this is not a drawback of technology. I have tried to simplify this technology for the purpose of understanding, we will take dive into detail in further.
Why do we need blockchain?
If we analyze the Indian banking system and its data structure of transactions, the data is located in the main centralized server where all the records of transactions are maintained and nodes are located in regions. If someone was to tamper the data by gaining unauthorized entry in the database by hacking or any other unethical way to get the personal benefit, he can do so by just making alteration in the main database. All other data centers (nodes) will be updated automatically as data is located in one location and its alteration possible.

How Blockchain addresses this problem?
Let's understand, What is Blockchain? Blockchain technology is the process of recording transactions through a dynamic distributed mechanism where each node gets updated on transactions in real-time automatically. It works on a decentralized approach where data is located on each node instead of a centralized location. So in case if anyone wants to alter the data, he needs to alter it at each location of nodes and that too in real-time which is impossible. In this way, it reduces the chances of getting tampered. There exist two keys namely public(known to public) and private(known to person only ), these work in pairs. Any transaction encrypted using one key can only be decrypted using others. For example to execute a transaction, one needs to encrypt a message consisting of instruction, the public key of the sender, and receiver using a private key. Then this message will be received by nodes in the blockchain network, nodes will verify the public attached to the message to know whether it meant for them or not. Further nodes will try to decrypt the message using the public key of the sender. Once decrypted, the message will be updated to all nodes. In this way, no one can enter the wrong information in the system. The transactions executed can’t be reversed and only new transactions can be entered in it. These transactions in a set known as block and their record of chains known as BLOCKCHAIN. The way blockchain is designed each node eats the reference made to it by the last node making it tough to trace the nodes where the transaction entered. This is how blockchain works.
Concept involved in blockchain operations
This is just an introduction, we will discuss them in detail in the next phase.
- HASH function: This is a function which converts the data character into a fixed number of strings and letter. The values are given by the hash function known as the hash value. The sender will send a file and its hash value, the intended receiver will apply the same hash function and compare the generated hash value with the received hash value. If the hash value is the same then the information is right.
- Nonce: This refers to adding a number at the end of data script/ instructions such that after hashing its hash value comes with two zeros in end. This makes for hackers more complicated to cheat out the hash function and decode the command.
- Encryption: Now we have a hash value with a hashed file that contains instructions to be performed. Next thing is to make this whole package unreadable by the unintended receiver by either some code. This code must be so strong that no unintended receiver can break it up but at the same time, we need to convey this to the needed receiver so that he can decrypt the code and perform the function. The problem is in making code which the receiver should know but the unintended person shouldn’t. Here comes in the picture system of crypto keys. Each node in the blockchain network has its public and private keys. These keys are used to encrypt the package of instructions. Once encryption is done by public keys of the sender it can only be decrypted by him using private keys which are only known to him. Now if the receiver wants to decrypt the instructions he needs to use his private key and sender’s public key.
- Digital signature: The sender before sending instruction need to be signed the instructions using his private keys to indicate ownership of command. This is called encrypted hash. Encrypted hash using the private key is sent along with the original data set. The receiver can decrypt using the public key of the sender and will create a hash of the message received. After comparing both he can check whether no unauthorized procedure is applied in between the signing of the message and receiving by him. As the same inputs give the same hash values.
- Proof of work: This refers to the time taken to validate the transaction placed in the blockchain network usually done by miners(nodes). The process involves the use of hit and trial methods to decrypt hash values. Hashed Set of Instructions encrypted using the private key of the sender and the public key of the receiver. Encryption
Mining: Miners are nodes which solve the proof of work and validate transaction to create blocks. These nodes get paid for creating blocks by solving the proof of works. Processing of proof of work directly depends on the number of fees, if the transaction has high fees then processing will be speedy. After knowing all the concepts involved in blockchain operations, let’s look further.
How transactions are executed in the blockchain network?
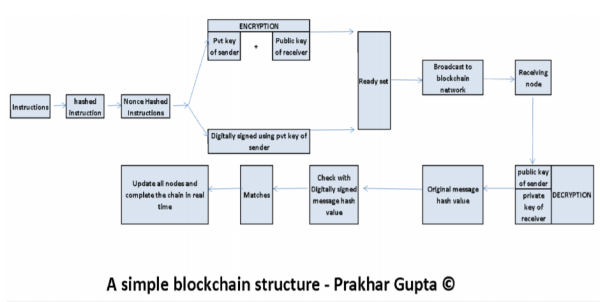
First, take an example, suppose Mr. Ram wants to send rs 10 to Mr. Shyam or we can say he wants to credit the ledger of Shyam and debit the ledger of him. The instruction is to pay rs 10 to Shyam, this will be first converted to hash value using a hash function into fixed no. of a string of letters. If the sender wants to be more secure he may use the nonce function by adding such numbers in the end of the instruction such that the hash value comes with two zeros in the end place. Now then the sender will use his private key and receiver’s public key to encrypt the instructions. Afterward this whole bundle will be digitally signed using the private key of the sender along with the original message. This whole set will then broadcasted to the blockchain network. The first node that will receive the message will try to validate the instructions by using the public key of the sender. One of the important protocol in the blockchain operations is input and output should always match, incase output is more than input (means you are trying to send more money than you existing account balance) transaction will be invalidated, if the output is less than input, the extra will be returned to sender after deducting the transaction fees. The nearest node will check whether the sender has sufficient balance in the account of the sender. After all such checks, it will run the bitcoin protocol and decrypt the instruction set using his private key and the public key of the sender. The node which will solve the hash value will get bitcoins as a reward to proof of work, this is the process of mining. After solving the hash value the instructions will be executed and block will be created. Here arises one case, suppose if Mr ram has rs 10 in his account and he tries to pay to two-person Shyam and Mohan at the same timers 10 each. We know blockchain is a distributed system of processing, ram can use two nodes at the same time to run the same command to pay Shyam and Mohan. Now whether he can pay to two having payment for one in his account in the blockchain. The answer is no, even if he will run two commands using two diff nodes, he can’t do so. The first node validating the proof of work will able to complete the transaction and the other one will get an error Now let’s discuss the global scenario and application of blockchain.
Application of blockchain:
1. Social media: In this era, data is said to be new gold but we hear daily that social media websites are leaking data daily. Thus there is a feeling of distrust among the people for using digital means. This new blockchain technology is based on a distributed system of processing where if any information attempted to the tampered the same need to tamper at all the nodes in real-time which is not possible. Blockchain is more secure and no transaction once done through it can be removed only added. This will also help to prevent usage of social media through fake id creation as it works on of encryption and hashing nonce which are a highly secure mediums for it.
2. Supply Management: We know that the cost record of any product is much sensitive, they are always prone to get leaked. The records of suppliers, customers, transporter, retailers, and employee are even important to the business. This will help businesses to grow without any hassle of data crises. Even data recovery is easy in blockchain as improper functioning of one node won’t down the whole system, data can be backed up from other nodes.
3. Security trading and stock exchange: In stock exchange for execution of the transaction, the seller gives a put for share and the buyer gives a call for share, stock exchange meanwhile works as an intermediary in between two parties. Usually, there is a time gap between order processing due to the existence of the intermediary. Time lag for price information, margin percentage to set off often get delayed due to transmission channel delay. Thus this gives rise to chances of arbitrage profit which is against the spirit of the stock exchange. Blockchain a technology that is decentralized and all information gets updated at all nodes within no time. Thus carrying out arbitrage is impossible in the blockchain. Moreover records all the stocks and their movement can be stored securely.
4. Identity solutions/ KYC: Today we have so many identity cards be it an adder or driving license or election’s identity or any other but it is equally tough to timely update all of them and make sure they are in safe hands. Blockchain allows merging them and creating a single window for all making it easy for authorities and holders to use them.
There is also some other usage of blockchain-like fast query handling and linking of information. Let's discuss a bit more about bitcoin, I am sure you should have got some idea of the nuts and bolts of blockchain. As per discussion, blockchain is a decentralized structure, there is no main body to process. Then who issues bitcoins, I mean there is a stock exchange for shares. Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency then who issues such currency. In fact blockchain is primarily used for data transfer, the nodes which decrypt the hash values get bitcoins as a reward of their efforts. These nodes then sell these bitcoins just similar to what we do for carbon credits. Concluding all this what I say that bitcoins and blockchain are very interesting technology and have great potential but there should be a regulatory framework to ensure the ethical working of blockchain and bitcoins. If I talk about the internet in the 1990s, hardly people would have believed me that it will become that important to us in the future, the same is the case with blockchain today.
The author is CA finalist, CRA -nism(sebi) and former assurance analyst at Grant Thornton India.










 CAclubindia
CAclubindia
