In this article, we will try to understand the GST Compliances in Transportation Sector.
1. INTRODUCTION
Transportation is the means to carry people and goods from one place to another. This has become essential in each stage of human civilization. Transportation has contributed the most to economic, social, cultural and political development and uplifting the nation, speedy industrialisation is nearly impossible without a robust transportation system.
Modes of transport in India are-
(i) Railways-faster transportation mode and also ideal for perishable goods, only rail haulage needs to be purchased through a freight company, third company logistics or a terminal operator
(ii) Roadways-Most common mode of transport. Generally, it is used for transportation of goods to both longer and shorter distances.
(iii) Waterways-it is an economical way to transport large volume of goods. But slow and not very much flexible like the other modes.
(iv) Airways- fastest mode of transport with some additional costs like security fees, handling charges, duty cost and taxes. Covers long distances in minimal time .
With the removal of inter- state check posts, GST enhances the supply chain and reduces the transportation cycle.

2. IS TRANSPORTATION A SUPPLY OF GOODS OR SERVICES?
As per Section 2 of CGST Act 2017, the definition of Services is as follows:-
As per sub section (102) ―"services" means anything other than goods, money and securities but includes activities relating to the use of money or its conversion by cash or by any other mode, from one form, currency or denomination, to another form, currency or denomination for which a separate consideration is charged"
As per sub section (52) ―" ‘goods" means every kind of movable property other than money and securities but includes actionable claim, growing crops, grass and things attached to or forming part of the land which are agreed to be severed before supply or under a contract of supply."
Hence, with the help of the above definitions, we can say that transportation falls under the category of supply of services.
3. TYPES OF TRANSPORTATION
2.1 Goods Transport Agency
Goods transport agency- as per section 65B (26) of finance act1994 and under GST law - clause (ze) of notification no.12/2017 - central tax (rate) defines GTA as any person who provides service in relation to transport of goods by road and issues consignment note ,by whatever name called.
Transport agency will be considered as goods transport agency only if, it issues consignment note.
Issuance of consignment note is sine- qua- non(essential) for the supplier of services to be considered as a goods transport agency.
Services rendered without issuance of consignment note are exempted under GST
CONSIGNMENT NOTE
Consignment note has not been defined in the CGST Act or in the Notification either.
As per Rule 4B of Service Tax Rules 1994
Consignment note has been defined as a document regarding the carriage of goods by road issued by the Goods Transport Agency
Issuance of consignment note indicates that the transfer of lien on the transporter .ie the transporter is now responsible for delivering the goods safely to its final destination.
Consignment note is serially numbered and must contains the following details:
- Name of consignor
- Name of consignee
- Registration number of the goods carriage in which the goods are transported
- Details of the goods
- Place of origin
- Place of destination
- Person liable to pay GST - consignor, consignee, or the GTA
Consignment note is an essential document but mere non issuance of it does not make the transaction exempt from GST. Nature of the activity which is being carried out is to be kept in mind
K M Trans Logistics Private Limited - AAR Rajasthan
[2019] 102 taxmann.com 212 (AAR - RAJASTHAN)
In the given case, the appellant K M Logistics Private limited was providing services to different manufacturers by delivering goods to their authorised dealers in various cities in India. Appellant was carrying e-way bill.
Appeal by the appellant
Appellant claimed that it is not liable to pay any GST as there is no consignment note has been issued only e-way has been issued and there is no such requirement in the e-way bill to mention the details about the consignment note. Since no consignment note issued services provided by its agency are not classified as the services of goods transport agency and does not fall under the purview of gst.
Facts of the Case
Format of e-way bill is not relevant for deciding the classification of services provided. Mere no mentioning of nay details in e-way does not affect the liability of payment of tax unless service has been exempted through a notification. Nature of activity is independent of the format of e-way bill.
Order of the Appeal
The appeal was rejected by the department and it was held that services provided by the appellant would be liable to GST.
Where applicant, a company, having registered office at Jaipur (Rajasthan) provides transport services and trucks/trailers used in providing such services are purchased in Rajasthan as well as registered with RTO Jaipur and billing, maintenance of accounts and operational control is done from Jaipur office, applicant's place of business for purpose of registration is at Jaipur
Where applicant, a company, having registered office at Jaipur (Rajasthan) provides transport services, since trucks/trailers used in providing such services are purchased in Rajasthan as well as registered with RTO Jaipur and billing, maintenance of accounts and operational control is done from Jaipur office, applicant is required to take registration ay Jaipur only
BON CARGOS PVT LTD vs ASSISTANT STATE TAX OFFICER
IN THE HIGH COURT OF KERALA
[2020-TIOL-2223-HC-KERALA-GST]
Facts of the Case
- In W.A. No.1735 of 2020, the detention was on 06.09.2020. The goods detained were covered by two invoices raised by the same consignor, one dated 04.09.2020 and the other dated 05.09.2020; respectively having value of Rs.33,748/-. The goods were carried together in one vehicle by the appellant, who is a Goods Transport Agency. There was no e-way bill accompanying the consignment.
- In n W.A. No.1736 of 2020 again the identical consignor had raised two separate invoices to the identical consignee with respective value of Rs.43,836/- and Rs.11,593/-; both dated 17.08.2020. The consignor generated eway bills for the two invoices, but the appellant-Transport Agency did not update part B of the e-way bill. The above goods were also transported in the same vehicle together and was detained for reason of there being no e-way bill accompanying the goods.
Appeal by the appellant
- The violation alleged according to the appellant cannot be sustained, since Rule 138 provides only for generation of e-way bill with respect to movement of goods of consignment value exceeding Rs.50,000/-. At the outset it is to be noticed that it is not the invoice value that provides the limit.
Order of the Appeal
- Explanation 2 defines the consignment value of goods to be that declared in an invoice, a bill of supply or a delivery chalan including the goods and services tax payable with any Cess charged. Sub-Rule (1) read with Explanation 2 leads to only one inference that the consignment value has to be determined from the invoice. But when goods of the same consignment covered by multiple invoices exceed the limit of Rs.50,000/-, necessarily there should be generation of e-way bill. Otherwise the mandate for generation of an e-way bill would be defeated and rendered redundant enabling the consignors to issue any number of bills having value below Rs.50,000/- and consign them in one vehicle.
- The consignment value is that shown in the invoice. When goods of the same consignor covered by different invoices are consigned together in one vehicle; the value will be the total of that in the multiple invoices. We are hence not satisfied that the detention was without jurisdiction.
2.2 PASSENGER TRANSPORT SERVICE
Passenger transportation services means conventional public transit service which operates on a fixed route and is available to public for a fare, intercity bus transportation, vanpools, subscription buses ,tour and charter bus transportation, bus transportation of pupils for educational purposes, taxi cabs licensed to conduct business in a municipality ,air and rail passenger service except for air charter services, and special transportation services for the elderly or persons with disabilities.
4. PLACE OF SUPPLY FOR TRANSPORTATION OF SERVICES
The term “Place of supply" has an essential role for the tax determination. As it helps us to understand that where the tax should be charged or from whom the tax should be collected.
Place of supply helps to determine whether IGST, CGST OR SGST will apply.
Place of supply depends upon:-
- Whether supply is intra-state i.e., transfer of goods o services within the state OR
- Inter state.ie., transfer of goods or service between two different states.
Basically, Place of Supply means place of delivery of goods or consumption of service. Transportation sector has three different parts, and the place of supply will be different for each one of them
Parts of transportation:
- Transportation of goods
- Transportation of passengers
- Services supplied on board a conveyance
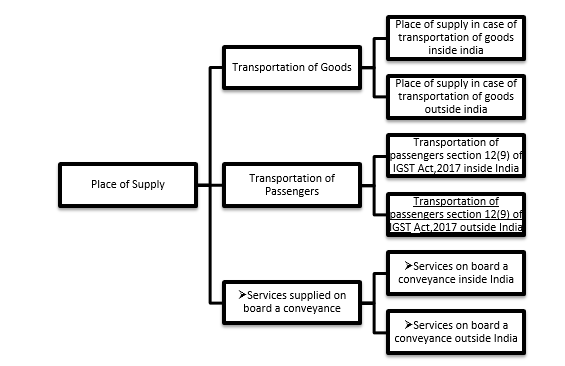
4.1. TRANSPORTATION OF GOODS
4.2.1 PLACE OF SUPPLY IN CASE OF TRANSPORTATION OF GOODS INSIDE INDIA
As per Section 12(8) of IGST ACT, 2017 the place of supply of services by way of transportation of goods , including mail or courier to
- When the supply is being made to registered person - place of supply would the location of the registered person
- When supply is being made to unregistered person -place of supply would be the place where goods are handed over for their transportation.
4.1.2. PLACE OF SUPPLY IN CASE OF TRANSPORTATION OF GOODS OUTSIDE INDIA :
Place of supply of services other than by mail or courier would be the place of destination of transported goods.
4.2. Transportation of passengers
4.2.1. TRANSPORTATION OF PASSENGERS SECTION 12(9) OF IGST ACT,2017 INSIDE INDIA
When supply is made to registered person- place of supply will the location of the registered person.
- When supply is being made to unregistered person-place of supply would be the place where the passenger embarks on the conveyance for a continuous journey:
[in case where the right to passage is given for future use and the point of embarkation is not known at the time of issue of right to passage, the place of supply of such service shall be determined in accordance with the provisions of -section 12 (2).
As per section 12(2) will be-
(a) if supply is made to registered person - place of supply would location of registered person
(b) if supply is made to unregistered person,--
(i)place of supply would be of the location of the recipient if address is available on records.
(ii) place of supply would be the location of supplier in any other case.
4.2.2. TRANSPORTATION OF PASSENGERS SECTION 12(9) OF IGST ACT,2017 OUTSIDE INDIA:
Where transportation of passengers takes place outside India place of supply of services would be the place where passenger embarks on the conveyance for continuous journey.
4.3. SERVICES SUPPLIED ON BOARD A CONVEYANCE
4.3.1. SERVICES ON BOARD A CONVEYANCE INSIDE INDIA
As per Section 12(10) , place of supply in case of services on board a conveyance ,including a vessel, an aircraft ,train or motor vehicle would be location of the first scheduled point of departure of that conveyance for the journey.
4.3.2. SERVICES ON BOARD A CONVEYANCE OUTSIDE INDIA
Place of supply in case services on board a conveyance , wholly or substantially consumed would be the first departure point of the conveyance
SECTION 13 OF IGST ACT- DETERMINATION OF PLACE OF SUPPLY OF SERVICES WHEN LOCATION OF SUPPLIER /RECIPIENT IS OUTSIDE INDIA
Place of supply under this case except services specified under section 13(3) would be service recipient" location. and if in any case the service recipient"s location is not available then place of supply would be supplier"s location
5. TIME OF SUPPLY OF SERVICES IN CASE OF TRANSPORTATION
Time of supply means the time when goods /services are considered supplied. Identification of time of supply is of utmost importance as it helps us to determine rate of tax, value and due date for payment of taxes.
Section 13 of CGST ACT, 2017 deals with the time of supply of services
Time of supply shall be earliest of the following:
In case where invoice is issued by the supplier within the prescribed limit:-
(i) date of issue of invoice issued by the supplier
OR (ii) date of receipt of payment(.i.e., date on which payment in entered in the books of supplier or credited in his accounts)
In case where invoice is not issued within the prescribed limit:-
- The date of provision of service OR
- date of receipt of payment
in case where both the above options are not available :-
- Date on which the receipt of services has been shown in books of accounts of service recipient.
- Time of supply in case where the supplier receives upto one thousand rupees in excess of the tax invoice :
- Time of supply would be date of issue of invoice, at the option of supplier
TIME OF SUPPLY IN REVERSE CHARGE MECHANISM
In case of Reverse charge mechanism- The liability to pay the tax is upon the service recipient instead of the supplier.
As per section 13(3) of CGST ACT 2017
Time of supply would be earliest in the following:
- payment date as entered in the books of Accounts of the service recipient or, date on which the service recipient"s account shows debited, whichever is earlier OR
- date immediately following 60 days from the date of issue of invoice or any other document by whatever name called, in lieu of thereof by the supplier.
IN CASE WHERE DETERMINATION OF TIME OF SUPPLY IS NOT POSSIBLE
Where determination of time of supply is not possible for certain circumstances, time of supply would be the date on which the entry has been made in Accounts book of Service Recipient.
6. EXEMPTIONS UNDER TRANSPORTATION
Exempt supply defines those supplies which have nil tax rate or fully exempt under section 11 or section 6 of IGST Act . It includes non-taxable supply.
Transportation of goods by Road
As per notification no.12/2017 -Central tax (rate) dated 28.06.2017 the following services are exempt from GST
- Services by way of transportation of goods by Road( heading 9965) and
- Services by way of inland waterways
But, if services of transportation of goods by road are provided by Goods transport Agency or Courier Agency, then GST is attracted.
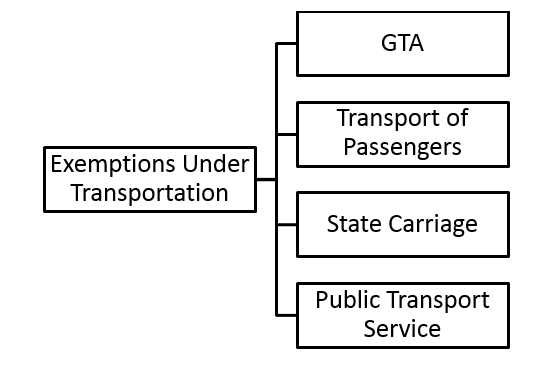
6.1. EXEMPTIONS IN CASE OF GTA
Following services falls under the category of exempt services as per Notification no.12/2017-Central Tax (rate) dated 28/06/2017:
- Single carriage upto one thousand five hundred rupees.
- Single consignee upto rupees seven hundred and fifty.
- Agricultural produce
- Milk, salt and food grain including flour , pulses and rice.
- Organic manure.
- Newspaper or magazines registered with the Registrar of Newspaper.
- Relief materials meant for victims of natural or man -made disasters, calamities, accidents or mishap
- Defense or military equipment.
One more exemption was allowed vide Notification No. 28/2018- Central Tax (Rate) (a) dated 31st December 2018 which states that freight charges in India is would be exempt from GST for the followings:
- Department or Establishment of the Central Government or State Government or Union territory; or
- Local authority; or
- Governmental agencies
which has taken registration under the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 (12 of 2017) only for the purpose of deducting tax under Section 51 and not for making a taxable supply of goods or services.
6.2. EXEMPTION IN CASE OF TRANSPORT OF PASSENGERS
As per notification no.12/2017-Central tax (rate) dated 28th june,2017 following services are exempt.
- GST Exemption for Transport Services in North-East States transport of passengers with or without accompanied belongings by air, embarking from terminating in an airport in the state of Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, or Tripura or at Bagdogra located in West Bengal
- Exemption to Contract Carriage
- Transport of passengers with or without accompanied belongings by non-air conditioned contract carriage other than radio taxi for passenger travelling excluding tourism conducted tour, charter, or hire is exempt from GST. IF contract carriage is air conditioned no exemption will be provided CARRIAGE CONTRACT- As per section 2(7) carriage means a motor vehicle which carries passenger or passengers for hire or reward and i engaged under a contract, whether expressed or implied, for the use of such vehicle as a whole for the carriage of passengers mentioned therein and entered into by a person with a holder of a permit in relation to such vehicle or any person authorized by him in this behalf on a fixed or an agreed rate or sum - (a)on a time basis, whether or not with reference to any route or distance; or(i) a maxi cab; and
- (ii) a motor cab notwithstanding the separate fares are charged for its passengers.
- (b) from one point to another, and in either case, without stopping to pick up or set down passengers not included in the contract anywhere during the journey, and includes -
6.3. EXEMPTION TO STATE CARRIAGE
Transport of passengers, with or without accompanied belongings, by stage carriage other than air-conditioned stage carriage is exempt from GST.
As per section 2(40), Stage carriage means a motor vehicle constructed or adapted to carry more than six passengers excluding the driver for hire or reward at separate fares paid by or for individual passengers, either for the whole journey or for stages of the journey.
(iv) Exemption in case of Public Transport Services
Service of transportation of passengers, with or without accompanied belongings, by
(a) railways in a class other than (i) first class or (ii) an air-conditioned coach;
(b) metro, monorail or tramway
(c) inland waterways
d) public transport, other than predominantly for tourism purpose, in a vessel between places located in India and
(e) metered cabs or auto rickshaws (including e-rickshaws). is exempt from GST.
Metered Cabs
Metered cab means any contract carriage on which an automatic device, of the type and make approved under the relevant rules by the State Transport Authority, is fitted which indicates reading of the fare chargeable at any moment and that is charged accordingly under the conditions of its permit issued under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 (59 of 1988) and the rules made thereunder (but does not include radio taxi).
Radio Taxi
Radio taxi means a taxi including a radio cab, by whatever name is called, which is in two-way radio communication with a central control office and is enabled for tracking using the Global Positioning System or General Packet Radio Service.
State Transport Undertaking
State transport undertaking" has the same meaning as assigned to it in clause (42) of section 2 of the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 (59 of 1988). As per section 2(42), State transport undertaking means any undertaking providing road transport service, where such undertaking is carried on by,-
(i) the Central Government or a State Government;
(ii) any Road Transport Corporation established under section 3 of the Road Transport Corporations Act, 1950 (64 of 1950);
(iii) any municipality or any corporation or company owned or controlled by the Central Government or one or more State Governments, or by the Central Government and one or more State Governments.
(iv) Zila Parishad or any other similar local authority.
"road transport service" means a service of motor vehicles carrying passengers or goods or both by road for hire or reward.
E-Rickshaw
E-rickshaw means a special purpose battery powered vehicle of power not exceeding 4000 watts, having three wheels for carrying goods or passengers, as the case may be, for hire or reward, manufactured, constructed or adapted, equipped and maintained in accordance with such specifications, as may be prescribed in this behalf.
(v) Transport Services To Central Government
Services provided to the Central Government, by way of transport of passengers with or without accompanied belongings, by air, embarking from or terminating at a regional connectivity scheme airport, against consideration in the form of viability gap funding is exempt from GST.
Provided that nothing contained in this entry shall apply on or after the expiry of a period of one year from the date of commencement of operations of the regional connectivity scheme airport as notified by the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
7. REGISTRATION UNDER TRANSPORTATION
As per section 22(1) of CGST Act, 2017 only if
- the aggregate turnover or taxable supply of goods and services in a state or union territory in a financial year exceeds 20 lakhs
- in case of special category states the amount is reduced to 10 lakhs.
Only in the above cases ,the concept of Registration come into picture.
As per section 23(1) of CGST Act 2017 those persons who supplies exempted goods/ services are not supposed to get themselves registered
As per Notification No.5/2017 Central tax dated 19-06-2017 , those taxable persons whose supplies falls under reverse charge mechanism are exempted from obtaining registration even if the aggregate turnover exceed (20 lakh/10 lakh)
As per section 24((i) of CGST Act2017 states that where taxable supply is being made from one state to another ( interstate supply) - registration is compulsory irrespective of the threshold limit.
8. RATE OF TAXATION
(A) IN CASE OF GOODS TRANSPORT AGENCY
The taxability can be of two types in case of GTA
(a) REVERSE CHARGE MECHANISM - IN CASE OF REVERSE CHARGE MECHANISM
- in this case, service recipient is require to pay the tax instead of the supplier which means GTA is not supposed to pay tax being a supplier .
- tax rate is 5% . service recipient will pay the tax and claim ITC but GTA will not be able to claim ITC -.
(b) FORWARD CHARGE MECHANISM- means when the tax is paid by the supplier
AS per Notification No.20/2017 Central Tax Rate 22nd August 2017 - This notification provides that if GTA opts to pay tax on forward charge basis then the tax rate would be 12%( 6% CGST & 6% SGST).
- In this case, GTA is also allowed to pay forward charge
- Rate of tax is 12% which can also be claimed by gta as tax paid on purchases
In this case, both service provider and recipient would be eligible to take input tax credit
(B) IN CASE OF PASSENGERS
1) GST on railways: 5% GST will be charged other the sleeper class in case of travelling through rail. Availment of input tax credit is allowed.
2) GST on Roadways
(a) renting of taxi or motor cabs- 18% gst will be charged and the fuel cost expenses will also be borne by the service recipient.
(b) air-conditioned contract or stage carrier (.i.e., buses ) and radio taxi -5% GST shall be charged and the availment of ITC is not allowed.
3) GST on Airways
- 5% GST is charged while travelling in economy class and ITC is also allowed.
- GST rate for transport of passengers with or without belongings by air, embarking from or terminating in a regional Connectivity Scheme Airport is also fixed @5% with input tax credit allowed on input services.
- GST rate is 12% Other than economy class. And ITC is also allowed
9. REVERSE CHARGE MECHANISM
(A) GOODS TRANSPORT AGENCY
Reverse charge is a mechanism where the recipient of goods /services is liable to pay GST instead of the supplier.
As per notification no. 13/2017 of Central Tax (rate) dated 28th June 2017 amended from time to time the following recipients of goods/services are liable to pay GST.
- Any factory registered under or governed by the Factories Act 1948
- Any Registered Society
- Any Co-Operative Society established by or under any law
- Any Company
- Any partnership Firm
- Association of Persons
- Any GST registered person
(B) PASSENGER TRANSPORT SERVICE
- Notification no.29/2019 CGST (Rate) and circular no.130/2019
- Reverse charge mechanism in applicable on transportation of passengers only in case of renting of motor vehicles carrying passenger.
- RCM will be attracted if the following three conditions are fulfilled;
- Supplier is other than a body corporate
- Supplier provides services to a body corporate
- Supplier doesn"t charge 12% GST on the invoice, 5% GST should be charged from the service recipient.
Renting of motor vehicles for transportation of passenger+ cost of fuel included in consideration
Example: ABC & Company enter into a contract with Mr. Raja, proprietor of Indian cabs services for receiving renting services of motor vehicle for it"s employees. Mr. Raja is charging 65000+5% of GST for the services
In the above case, ABC & company is liable to pay GST under RCM
10. RETURNS REQUIRED TO BE FILED
In case of goods transport agency the following returns are supposed to be filed:-
- GSTR 1: details regarding outward supplies. It can be filed both monthly or quarterly. Additionally Taxpayer can opt for Invoice Furnishing Facility (IFF) for first two months of the Quarter in case they opt for QRMP (Quarterly Return Monthly Payments)
- GSTR 3B: provides monthly summary and tax liability
- GSTR-9: Annual Return
- GSTR-9C: Reconciliation Statement if Turnover more than Rs. 2Cr/5Cr
11. ACCOUNTS AND RECORDS
As per Section 35 of CGST Act 2017 the following details shall be maintained in case of Transportation:
Registered parties shall keep at his principal office its registration certificate which provides true and correct account of the following:
- production or manufacture of goods
- inward and outward supply of goods/services/both
- stock of goods
- input tax credit availed
- output tax payable and paid and
- such other particulars as may be prescribed
- Registered party shall maintain records of the consignor, consignee and other relevant details of the goods in such manner as prescribed.
- Registered party may maintain such records in electronic form in uch manner as prescribed.
- Where the place of business is more than one and the same has been specified in the registration certification, accounts related to each place shall be kept at such places of business.
12. RETENTION OF RECORDS
- As per section 36 of CGST Act 2017, the registered person is require to retain the accounts or other records until the expiry of seventy two months from the due date of furnishing of annual return for the year.
- In case where the registered person is a party to an appeal or revision or any other proceedings before any appellant authority or Revisional authority or court whether initiated by himself or by commissioner is under investigation under chapter XIX- shall retain the records for one year or 72 days after disposal of such appeal or revision or proceedings, whichever is later.









 CAclubindia
CAclubindia
